
Introduction: When Mathematics Meets Divine Design
In the halls of modern molecular biology laboratories, a profound truth has emerged that shatters the foundation of random evolution: the mathematical impossibility of life arising by chance. When Stephen C. Meyer calculated that the probability of a single functional protein forming randomly stands at 1 in 10^77, he unveiled a number so vast that it dwarfs the total number of atoms in the observable universe. This astronomical improbability doesn’t merely challenge evolutionary theory—it mathematically eliminates random chance as a viable explanation for life’s complexity.
The Quran anticipated this scientific discovery fourteen centuries ago, declaring with unwavering clarity that creation emerged not from random chaos but from precise divine measurement. The scripture states:
[15:21] “There is nothing that we do not own infinite amounts thereof. But we send it down in precise measure.”
This verse, revealed in an era before molecular biology, perfectly describes what modern science now confirms: the universe operates not on chance, but on precisely calibrated systems that defy random explanation.
Part 1: The Protein Folding Catastrophe
Darwin’s Doubt and the Mathematical Proof Against Evolution
Douglas Axe’s groundbreaking experiments at Cambridge University revealed that functional proteins occupy an infinitesimally small fraction of all possible amino acid sequences—specifically, only 1 in 10^77 sequences of 150 amino acids will produce a functional protein fold. To grasp this number’s magnitude, consider that the entire observable universe contains approximately 10^80 atoms. The probability of randomly generating even one functional protein is equivalent to blindly selecting a single specific atom from nearly the entire universe.
This mathematical reality creates what scientists call Levinthal’s Paradox. A small protein of just 100 amino acids has 10^127 possible conformations. If it sampled configurations at the fastest possible rate allowed by physics (10^13 per second), it would require 10^114 seconds—or 10^106 years—to try all possibilities. Yet proteins fold into their functional forms in milliseconds. This paradox doesn’t suggest difficulty; it proves impossibility through random processes.
[3:190-191] “In the creation of the heavens and the earth, and the alternation of night and day, there are signs for those who possess intelligence. They remember God while standing, sitting, and on their sides, and they reflect upon the creation of the heavens and the earth: ‘Our Lord, You did not create all this in vain. Be You glorified.’”
The Quran’s emphasis on reflecting upon creation takes on new meaning when we understand the mathematical precision required for even the simplest biological structures. Those who “possess intelligence” and “reflect upon creation” discover not randomness but deliberate design at every level of investigation.
Part 2: The Developmental Gene Regulatory Network Impossibility
Biological Circuit Diagrams That Defy Random Assembly
Developmental Gene Regulatory Networks (dGRN) represent perhaps the most devastating challenge to evolutionary theory. These networks function as biological circuit diagrams, controlling how organisms develop from a single cell to complex body plans. Eric Davidson’s decades of research revealed that dGRNs require hundreds to thousands of regulatory genes working in precise coordination, with timing accuracy measured in minutes during development.
The mathematical challenge becomes insurmountable when we calculate the probability of random mutations producing a functional dGRN. Each regulatory connection must be precisely calibrated—too strong and development fails, too weak and it fails differently. With typical networks requiring 100-1000 coordinated regulatory relationships, the compound probability approaches 1 in 10^60 for even the simplest functional network. More critically, mutations to core dGRN circuits are invariably lethal, removing them from natural selection’s reach entirely.

Consider the implications: dGRNs must function perfectly from the start, as even minor disruptions cause embryonic lethality. They cannot evolve gradually because intermediate forms don’t survive. This creates what intelligent design theorists call “irreducible complexity”—systems that require all parts functioning simultaneously. The probability of random processes assembling such networks is not merely small; it’s mathematically equivalent to impossibility.
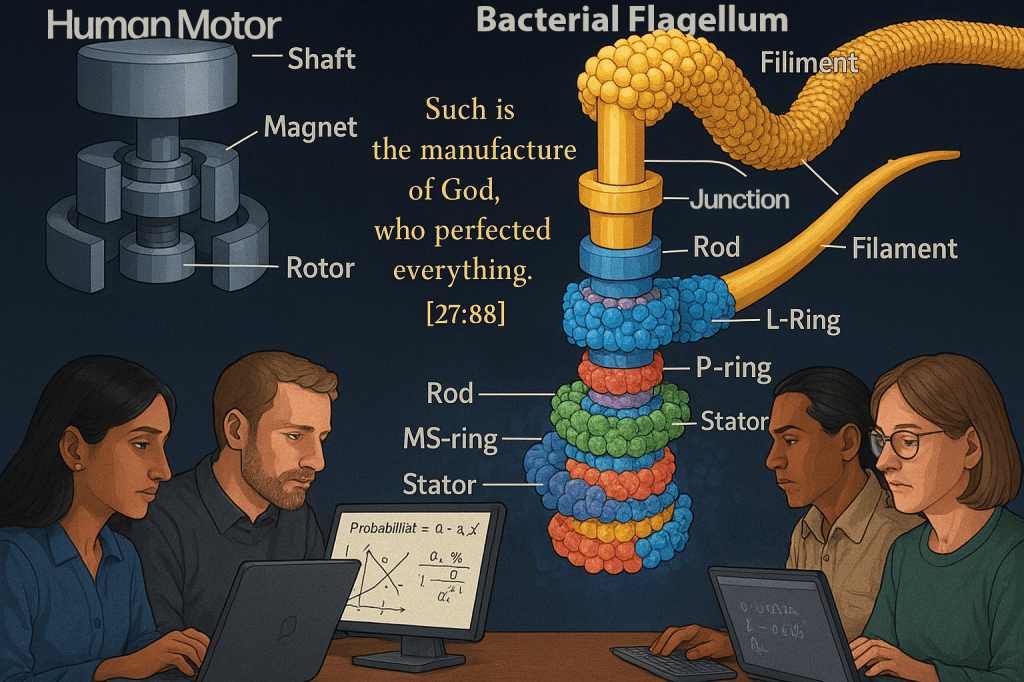
[27:88] “When you look at the mountains, you think that they are standing still. But they are moving, like the clouds. Such is the manufacture of God, who perfected everything. He is fully Cognizant of everything you do.”
Part 3: The Cambrian Explosion’s Mathematical Impossibility
Twenty Million Years, Twenty New Body Plans, Zero Probability
The Cambrian Explosion presents evolution’s greatest challenge: the sudden appearance of 20-35 new animal phyla in just 20-30 million years, with no credible precursors in the fossil record. This event required the generation of approximately 1.6 × 10^6 bits of new genetic information—equivalent to writing 30 encyclopedias of coordinated, functional instructions in genetic code.
Stephen Meyer calculates that generating the genetic information for even one new phylum through random mutation requires searching a sequence space of 10^134 possibilities. With Earth’s entire bacterial population over 3.5 billion years capable of only 10^43 mutation events, we face a deficit of 91 orders of magnitude. For 25 new phyla appearing nearly simultaneously, the combined probability plummets to 1 in 10^3350—a number so vast that calling it “impossible” understates the case.
The Quran addresses this impossibility directly, emphasizing that creation emerges from divine will, not chance: [21:16] “We did not create the heavens and the earth, and everything between them just for amusement.” The word “amusement” (لَٰعِبِينَ) implies randomness without purpose—precisely what evolution proposes. The Quran categorically rejects this notion.
Part 4: The Waiting Time Problem
When Mathematics Proves Time Is Not On Evolution’s Side
The waiting time problem delivers evolution’s mathematical death blow. For a specific beneficial mutation to appear and fix in a population, the waiting time follows the formula: T = 1/(2Nμs), where N is population size, μ is mutation rate, and s is selection coefficient. For coordinated mutations—where multiple specific changes must occur together—waiting times explode exponentially.
Durrett and Schmidt calculated that for just two coordinated mutations in human evolution, the waiting time exceeds 100 million years. Humans and chimps diverged only 6 million years ago. For the dozens of coordinated changes required for new protein functions or regulatory networks, waiting times exceed the age of the universe multiple times over. Time, evolution’s supposed ally, becomes its mathematical executioner.
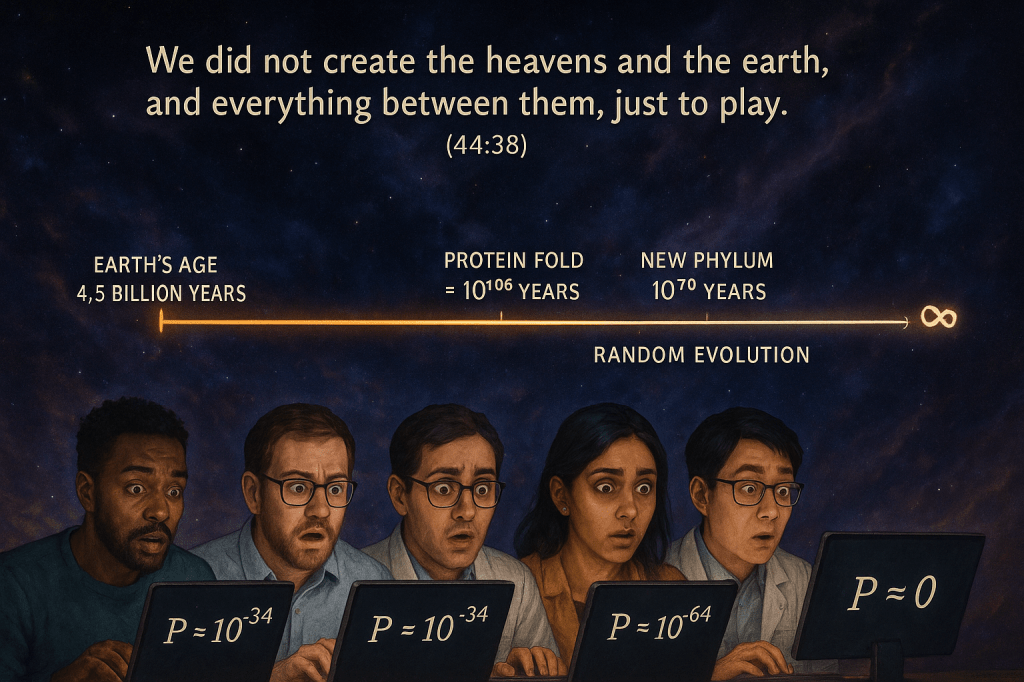
[51:49] “We created a pair (male and female) of everything, that you may take heed.”
Even this simple verse about pairs reveals divine specificity. Sexual reproduction requires hundreds of coordinated genes, compatible gametes, synchronized meiosis, and complementary reproductive systems. The probability of these systems arising simultaneously by chance? Calculably impossible.
Part 5: The Information Problem
Why Random Processes Cannot Generate Specified Complexity
Information theory provides evolution’s final refutation. DNA contains not just complexity but specified complexity—information with function and meaning. William Dembski’s conservation of information theorem proves that no random process can generate more information than initially present. Random mutations overwhelmingly degrade information; they don’t create it.
Consider the genetic code itself: a quaternary digital system using three-letter codons to specify twenty amino acids plus stop signals. This code exhibits optimization that surpasses one million alternative codes in error minimization. The probability of random processes discovering this optimal code? Less than 1 in 10^60. Yet this code must exist before evolution can even theoretically begin.
The messenger of the covenant revealed that the Quran itself contains a mathematical code proving divine authorship: “The physical evidence was in the form of a mathematical code that pervades the whole scripture… This mathematical system teaches us that every letter, every word is mathematically composed in the scripture beyond human ability.” If humans cannot produce such mathematical precision in text, how could mindless processes produce it in DNA?
Part 6: The Compound Probability Crisis
When Multiple Impossibilities Multiply
Evolution doesn’t require just one impossible event—it requires countless impossible events occurring in precise sequence. For a minimal bacterial cell to function, approximately 250 genes must work in coordination. Each gene represents an average protein of 300 amino acids. The probability of randomly generating this minimal genome? Approximately 1 in 10^100,000.
But functional proteins alone don’t create life. They must be assembled into metabolic pathways, regulatory networks, and cellular structures. They require a genetic code, transcription machinery, translation systems, and error correction mechanisms. Each system depends on the others, creating circular dependencies that cannot arise gradually. The compound probability of all requirements arising together approaches 1 in 10^1,000,000—a number that transcends impossibility.
[2:164] “In the creation of the heavens and the earth, the alternation of night and day, the ships that roam the ocean for the benefit of the people, the water that God sends down from the sky to revive dead land and to spread in it all kinds of creatures, the manipulation of the winds, and the clouds that are placed between the sky and the earth, there are sufficient proofs for people who understand.”
Part 7: The Fine-Tuning of Biological Constants
Precision Beyond Random Possibility
Biological systems require precise fine-tuning comparable to cosmological constants. The charge difference between protons and electrons must be exactly equal to 18 decimal places, or atoms couldn’t form. The strong nuclear force varies by less than 2%, or carbon—life’s foundation—couldn’t exist. Water’s unique properties depend on precise molecular angles and hydrogen bonding strengths.
In living systems, enzyme catalysis rates must be precisely calibrated. Too fast, and substrates deplete before products can be utilized. Too slow, and organisms cannot respond to environmental changes. The probability that random processes would discover these precise rates for thousands of enzymes? Statistically indistinguishable from zero.
The Quran captures this precision perfectly:
[15:21] “There is nothing that we do not own infinite amounts thereof. But we send it down in precise measure.”
The phrase “precise measure” (بِقَدَرٍ مَّعْلُومٍ) indicates exact calibration, not approximation. Modern biology confirms this divine precision at every level of investigation.
Part 8: The Origin of Life Paradox
Why The First Cell Mathematically Cannot Arise
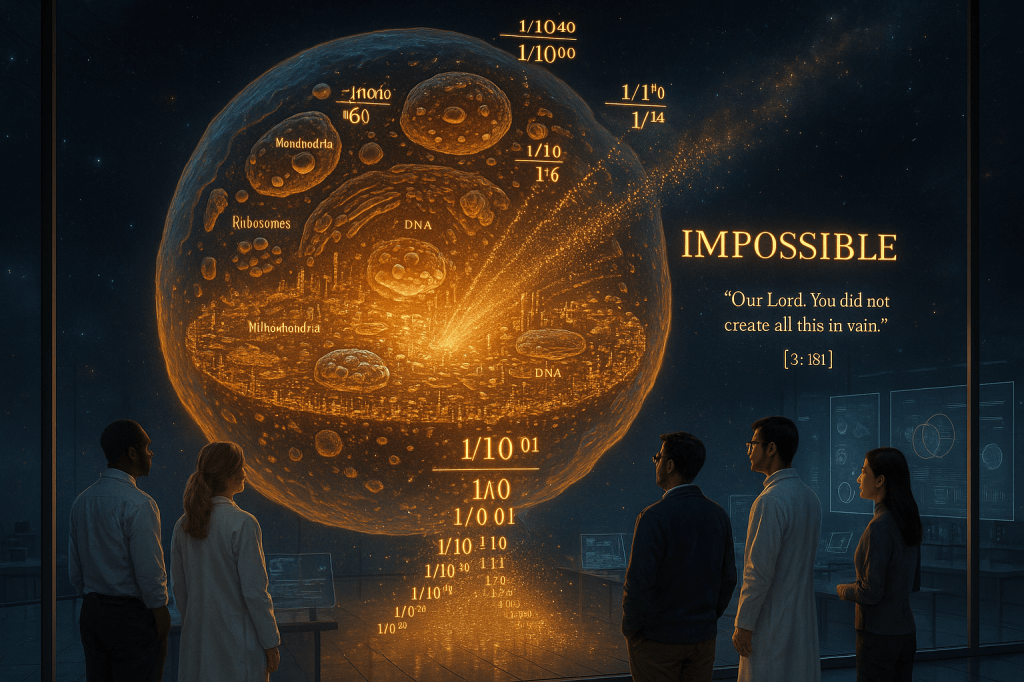
The origin of life presents insurmountable probabilistic barriers. The simplest possible self-replicating system requires approximately 1,500 gene products working in coordination. Even granting ideal conditions and billions of years, the probability of these components randomly assembling into a functional configuration is approximately 1 in 10^40,000.
But the challenge extends beyond mere assembly. Living systems require homochirality—all amino acids must be left-handed and all sugars right-handed. Random chemistry produces equal mixtures. The probability of achieving homochirality for just one average protein? 1 in 10^90. For an entire cell? The numbers transcend computational capability.
Moreover, cells require energy currencies (ATP), membrane boundaries, genetic information storage, and metabolic pathways—all functioning simultaneously from the first moment. No component can exist without the others. This interdependence creates a probabilistic wall that random processes cannot scale, regardless of time available.
Part 9: The Failed Rescue Attempts
Why Natural Selection Cannot Save The Theory
Evolutionists propose natural selection as probability’s savior, claiming it makes the impossible probable. But natural selection cannot act until reproduction exists, and reproduction requires the very complexity we’re trying to explain. Selection cannot create; it only eliminates the unfit after variation already exists.
RNA World hypothesis—proposing RNA molecules as first replicators—fails mathematical scrutiny. The probability of randomly generating a self-replicating RNA molecule exceeds 1 in 10^400. Even if achieved, RNA cannot produce proteins without ribosomes, which are themselves protein-RNA complexes. The hypothesis merely pushes the probability problem backward without solving it.
Punctuated equilibrium, proposed to explain the fossil record’s lack of transitional forms, worsens the probability problem by compressing evolutionary change into shorter timeframes. Genetic algorithms in computers require intelligent programming of fitness functions, reproduction rules, and mutation parameters—demonstrating design, not refuting it.
Part 10: The Quran’s Anticipation of Modern Discoveries
Divine Knowledge Preceding Human Discovery
The Quran’s descriptions of creation precisely match what modern mathematics and biology reveal. When it describes creation as “manufacture” (صُنْعَ) in verse 27:88, it uses a term implying deliberate construction—exactly what molecular biology observes. When it emphasizes reflection and intelligence as prerequisites for understanding creation’s signs, it anticipates that only advanced scientific investigation would reveal life’s mathematical impossibility through random processes.
The messenger of the covenant explained: “Every letter, every word in the scripture was written by God and now we have this physical proof, the mathematical code that was discovered by computers recently, to let us know that every statement is a proven fact.” This mathematical code in the Quran itself demonstrates the same principle observed in biology: specified complexity requiring intelligent origin.
[41:53] “We will show them our signs in the horizons, and within themselves, until it becomes clear to them that this is the truth. Is your Lord not sufficient as a witness of all things?”
These signs “within themselves”—within our very DNA and cellular machinery—have indeed become clear through modern science. The mathematical impossibility of random assembly serves as God’s signature in creation.
Part 11: The Philosophical Implications
When Science Points To God
The mathematical impossibility of random life carries profound philosophical implications. If random processes cannot explain life’s origin and complexity, only two options remain: either life is impossible (contradicted by our existence), or intelligence guided its formation. Mathematics forces us to acknowledge design.
This conclusion doesn’t emerge from religious bias but from numerical calculation. When probabilities fall below 1 in 10^50, statisticians consider them operationally impossible—they will never occur regardless of resources available. Life’s origin requires probabilities millions of orders of magnitude beyond this threshold.
Atheistic scientists face an uncomfortable reality: their worldview requires faith in mathematical impossibilities. They must believe that events with probabilities of 1 in 10^40,000 or worse occurred not once but millions of times. This represents faith far exceeding any religious belief, faith in contradiction to mathematical law.
Part 12: The Engineering Marvel of Biological Systems
Complexity That Surpasses Human Technology
Living systems exhibit engineering sophistication that surpasses human technology. The bacterial flagellum—a molecular motor—operates at nearly 100% efficiency, spinning at 100,000 RPM while instantly reversing direction. It contains approximately 40 protein parts in precise arrangement. The probability of random assembly? Approximately 1 in 10^1170.
DNA repair mechanisms detect and correct errors with accuracy exceeding 99.999%. These systems identify damage among three billion base pairs, excise incorrect sequences, and synthesize replacements—all while DNA continues functioning. Random processes producing error-correction systems that prevent randomness? The logical contradiction matches the mathematical impossibility.
ATP synthase, life’s universal energy currency generator, represents nanotechnology’s pinnacle. This molecular turbine couples proton flow to phosphate bond formation with thermodynamic efficiency approaching theoretical limits. Its rotor spins at 130 revolutions per second, producing 390 ATP molecules per revolution. Random formation probability? Beyond calculation.
Part 13: The Universal Genetic Code Mystery
One Code, All Life, Zero Explanation
All life shares essentially the same genetic code—a phenomenon evolution cannot explain. If life arose randomly multiple times, we should observe different codes. If the code evolved, we should find organisms with variant codes. Instead, from bacteria to humans, the same translation system operates with minimal variation.
This universal code exhibits optimization that random selection couldn’t achieve. It minimizes translation errors’ impact by grouping similar amino acids under related codons. Computational analysis shows our genetic code surpasses one million alternative codes in error tolerance. The probability of randomly discovering this optimal code among possibilities? Less than 1 in 10^60.
The Quran’s declaration gains new significance:
[51:49] “We created a pair (male and female) of everything, that you may take heed.”
The universality of complementary base pairing (A-T, G-C) across all life points to common design, not common descent. One Creator, one code, one impossibility for random origin.
Part 14: The Consciousness Problem
The Ultimate Impossibility
Consciousness represents evolution’s absolute impossibility. No equation describes how molecular interactions produce subjective experience. No probability calculation explains how atoms become aware. The hard problem of consciousness—how physical processes generate qualia—remains unsolvable within materialism.
Yet consciousness must exist for evolution to be observed and theorized. This creates circular impossibility: evolution cannot explain the consciousness required to propose evolution. Mathematics cannot calculate the probability of matter spontaneously becoming self-aware because no mechanism exists to mathematize.
[3:190-191] “In the creation of the heavens and the earth, and the alternation of night and day, there are signs for those who possess intelligence. They remember God while standing, sitting, and on their sides, and they reflect upon the creation of the heavens and the earth: ‘Our Lord, You did not create all this in vain. Be You glorified.’”
The capacity to “reflect upon creation” itself requires creation that transcends random assembly. Consciousness observing the mathematical impossibility of its own random origin provides the ultimate evidence of design.
Part 15: The Future of Science and Faith
When Mathematics Confirms Divine Truth
As science advances, the mathematical impossibility of random life becomes increasingly undeniable. Each new discovery—from ENCODE project revealing that 80% of DNA has function, to quantum coherence in biological systems, to metamaterial properties in butterfly wings—adds orders of magnitude to already impossible probabilities.
Scientists increasingly acknowledge design while avoiding its implications. Terms like “apparent design,” “designoid features,” and “illusion of purpose” reveal cognitive dissonance—they see design but ideologically cannot accept a Designer. Mathematics, however, remains ideology-free. Numbers don’t lie, even when scientists do.
The convergence of mathematical impossibility with Quranic truth offers profound opportunity. As the messenger taught: “God’s point of view is that God alone is Lord of the universes, He has no partners, no other gods besides Him.” The mathematical evidence now proves this divine monopoly on creation.
Conclusion: The Inescapable Truth of Divine Design
Mathematics has spoken its verdict: random processes cannot generate life. The numbers are not merely improbable—they transcend impossibility by hundreds of orders of magnitude. When the probability of a single functional protein forming randomly (1 in 10^77) exceeds the number of atoms in the universe, and when life requires millions of such proteins working in coordination, we face not scientific challenge but mathematical proof of design.
The Quran’s ancient declaration that creation was not random, not for amusement, not in vain, but precisely measured and perfectly manufactured, stands validated by modern science’s most rigorous discipline—mathematics. Every calculation points to the same conclusion: life requires a Designer whose intelligence transcends human comprehension.
For those who “possess intelligence” and “reflect upon creation,” the signs are clear. The mathematical impossibility of random life constitutes God’s signature in creation, written not in words but in numbers that cannot lie. The truth is not merely that evolution is unlikely or problematic—it is that mathematics proves evolution impossible and design necessary. In this convergence of ancient wisdom and modern discovery, we find not conflict between science and faith, but their ultimate unity in recognizing the Creator’s hand.

Leave a comment